Early versions of NetBird maintained persistent WireGuard connections between peers. This approach kept WireGuard connections open even if there was no actual traffic, consuming unnecessary resources on the devices. As a result, maintaining continuous peer connections can lead to scalability issues and inefficient performance, particularly within large-scale or resource-constrained environments.
NetBird has introduced a new feature called lazy connections to address these challenges. This feature allows NetBird to establish peer connections only when there is actual network activity, significantly improving network efficiency and resource utilization.
What Are Lazy Connections?
The lazy connections feature greatly improves how NetBird handles connectivity. Instead of constant connections, peers now connect on-demand, and are activated by network activity such as pinging a remote peer, or accessing an internal resource via a browser, ssh, etc. When enabled, lazy connections:
- Establish connections only when required.
- Monitor activity, automatically disconnecting peers that become inactive.
Benefits for Your Network
Lazy Connections significantly improve network performance and resource efficiency. By activating connections only as needed, the feature:
- Reduces unnecessary network overhead.
- Conserves valuable system resources, crucial for IoT and mobile environments.
Getting Started
Enabling Lazy Connections is straightforward:
-
Via environment variable:
-
Via CLI:
-
Or easily through the NetBird Dashboard:
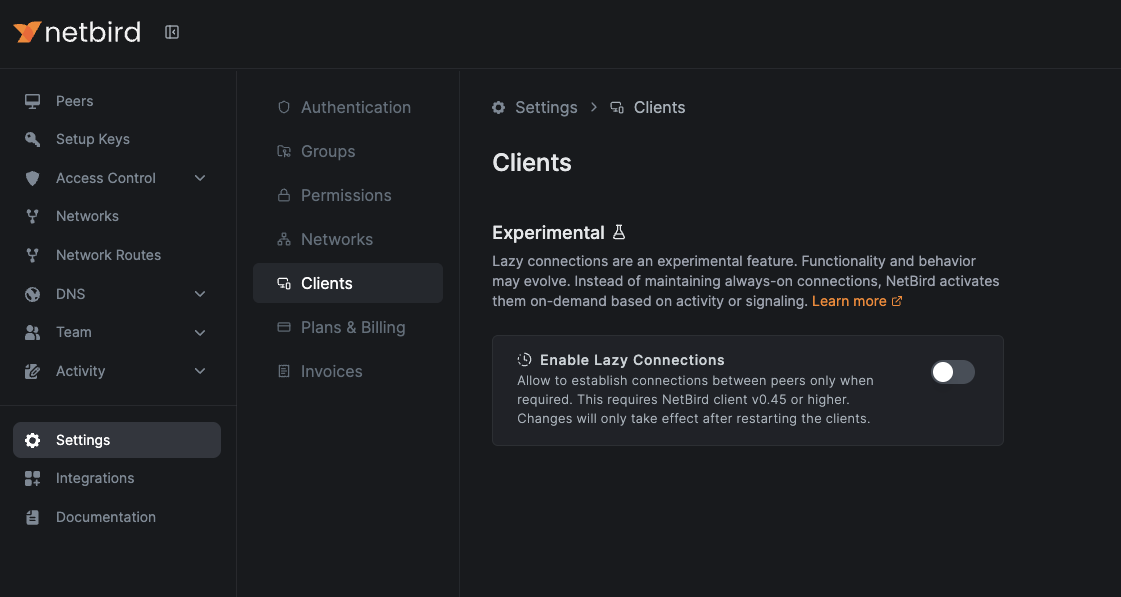
Ensure your NetBird agent and Management server are updated to version 0.45.0 or higher.
Looking Ahead
NetBird continues to refine Lazy Connections, enhancing disconnection logic and supporting resource access via routing peers. Your feedback helps shape these improvements.
Explore the Lazy Connections documentation .
